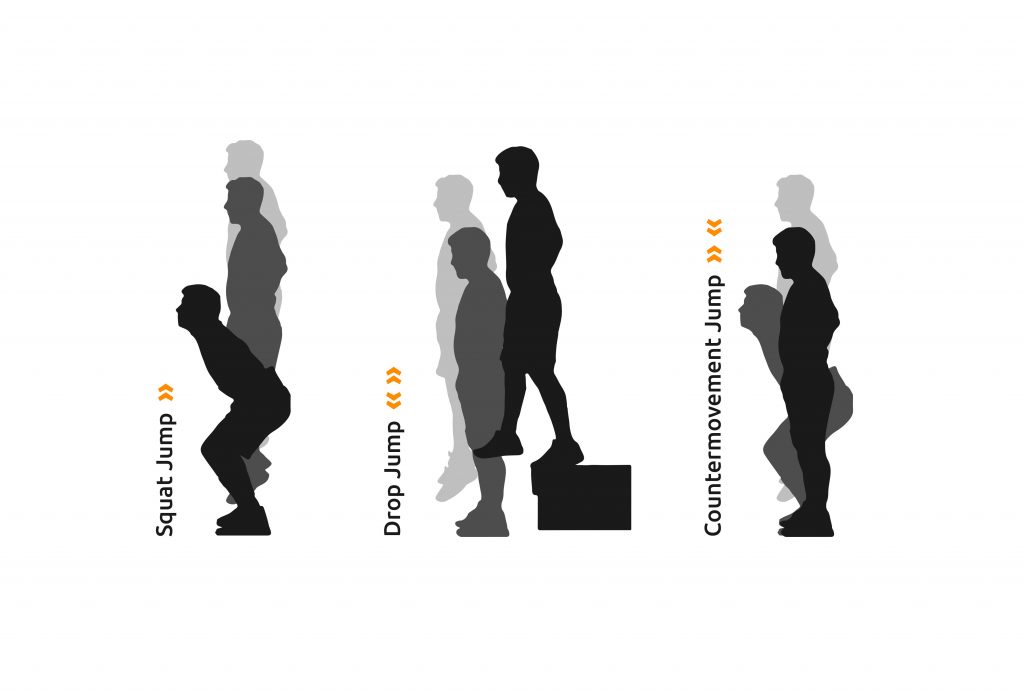
From a sporting perspective, jumping power is a sub-function of springiness, which is directly performance-dependent. The standard jump test is a scientifically established method for recording the springiness behavior of the leg extension chain. This test includes the Drop Jump (DJ), Countermovement Jump (CMJ) and Squat Jump (SJ). In all of the vertical jumps mentioned, an attempt is made to reach the maximum jump height.
We
recommend that you perform the jump tests in the following order:
1. Squat Jump (SJ)
2. Drop Jump (DJ)
3. Countermovement Jump (CMJ)
In this order the data of the jumps are more unique and can be evaluated better afterwards.
Attention
– The hands remain on the hips during the jump to reduce the effect of the arms, which can be used to increase height during the jump.
– Before and after each jump, a standing time of at least 1 second should be observed.
– The jump tests are performed without SmarTracks Timing Gates.
Squat Jump
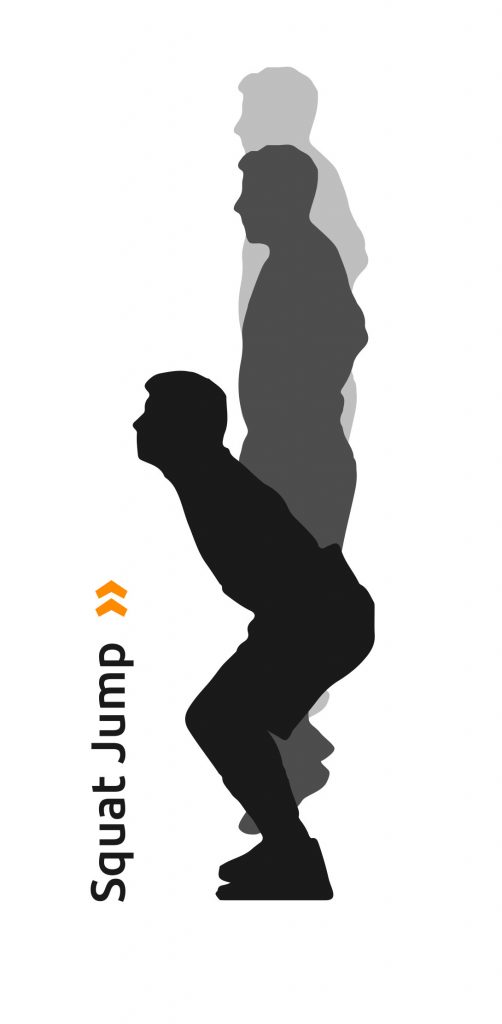
The Squat Jump (SJ) is a vertical jump in which the concentric force of the jump musculature is tested from the squat position without counter movement.
How to jump correctly:
The upper body is slightly bent forward in the starting position, the knees are bent 90°. The hands remain on the hips during the jump to reduce the effect of the arms, which can be used to increase height during the jump. The exercise consists of jumping as high as possible from the starting position, without any counter-movement at the start of the jump.
What is measured?
Jump height (cm)
How to find the test results in the software
The test results are displayed in the Diagnostics Software under the “Jumps” tab.
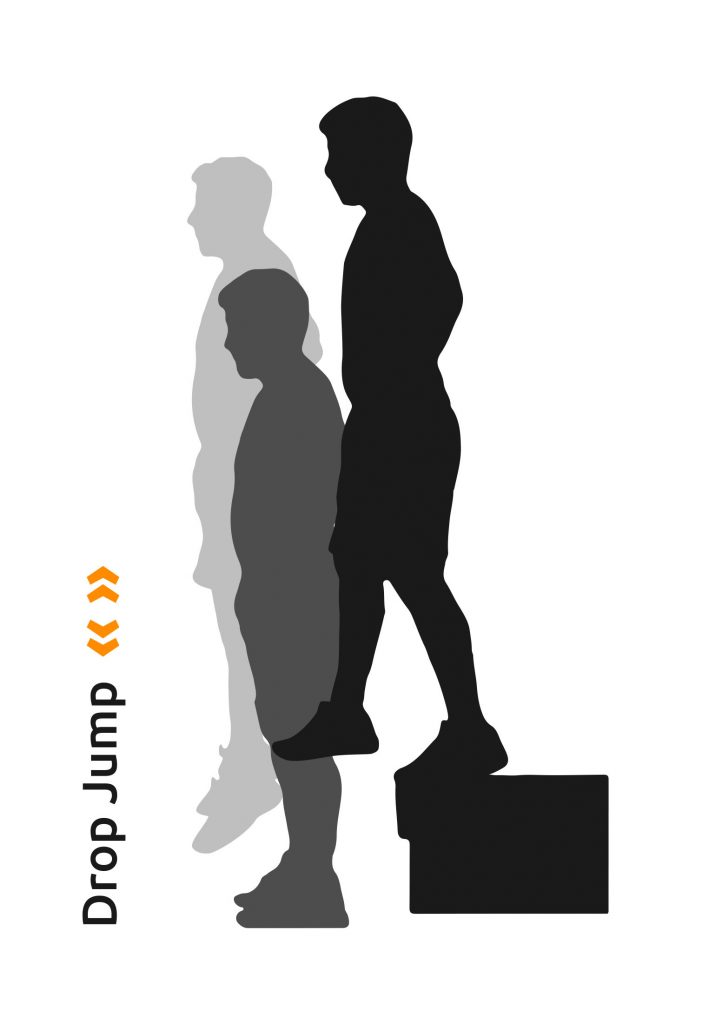
Drop Jump
The Drop Jump (DJ) is a vertical jump in which the muscles undergo a so-called stretch-shortening cycle. This characteristic makes it possible to assess the Reactive Strength Index of the jumping muscles, which is a reliable indicator of an athlete’s general bounce.
How to jump correctly:
In a drop jump, the athlete goes down from a box or platform and immediately after landing jumps up as high as possible to keep ground time and horizontal movement as low as possible. After the jump, you should arrive in an upright position without bouncing excessively on your knees. Keep your hands on your hips during the jump to minimize the effect of your arms, which can maximize your jump height.
The Drop Jump is usually repeated with different heights of the platform or box. The drop height is usually raised in 15 or 20 cm (6″ or 8″) increments and the optimum height depends on the athlete’s ability to absorb and transform the forces that occur.
What is measured?
In addition to the step height, a short contact time with the ground is also measured, then a Reactive Strength Index (step height divided by ground contact time) can be calculated. The impact velocity and the energy input into the muscles used for jumping are changed by varying the height of fall and the performance (height of jump or the ratio of height of jump to contact time on the ground) is maximized with optimal input (height of fall).
– Step height (cm)
– Ground contact time (ms)
– Reactive Strength Index (step height [cm] / Ground contact time [s])
How to find the test results in the Software
The test results are displayed in the Diagnostics Software under the “Jumps” tab.
Countermovement Jump

The Countermovement Jump (CMJ) is a vertical jump for testing the concentric force in the jump musculature.
How to jump correctly:
The CMJ consists of jumping from an upright position as high as possible after making a counter-motion at the start of the jump. The counter-movement is a rapid downward movement to the starting position of the squat jump, followed by a high jump to the upside.
The hands are held on the hip during the jump to reduce the effect of the arms, which can be used to increase the height when jumping.
What is measured?
Jump height (cm)
How to find the test results in the software
The test results are displayed in the SmarTracks softwareunder the tab “Jumps”.

